Inclusive regional economic development (IRED)
Inclusive Regional Economic Development (IRED) is a strategic approach that integrates economic growth with equity and inclusion.
It is both a process and an outcome, ensuring that economic benefits reach historically marginalized communities through coordinated cross-sector strategies. Key principles include:
Collaboration: Mobilizes diverse partners across sectors and geographies.
Equity & Inclusion: Embeds community leadership and participation in economic initiatives.
Resilience: Builds adaptable local economies that can withstand economic shifts and challenges resilient local economies that benefit people, places, and industries.
Achieving equitable economic development requires addressing the complex forces that contribute to systemic inequities. This means rethinking traditional approaches, fostering cross-sector partnerships, and building strategies that ensure all communities have access to economic opportunity. Inclusive economic development goes beyond business attraction and expansion; it prioritizes equity, economic resilience, and shared prosperity.
Traditional economic development often benefits regions with pre-existing advantages, leaving marginalized communities behind. Inclusive Regional Economic Development (IRED) integrates economic strategies with equity-focused solutions, ensuring coordinated investments and sustainable growth. It emphasizes collaboration, inclusion, and systemic change to create economies that serve everyone. The goal of IRED is to align economic, human capital, and place-based development efforts to create thriving, inclusive economies.
Implementing IRED
To implement IRED effectively, communities and leaders should consider:
CLEAR GOALS – Define intended outcomes and strategic priorities.
CAPACITY TO IMPLEMENT– Establish crosssector partnerships, align resources, and create systems for sustainability.
DEFINED EQUITY AND INCLUSION TARGETS – Identify who benefits and ensure equitable access to opportunities.
INVESTMENT READINESS – Secure and align diversified funding sources for long-term economic resilience.
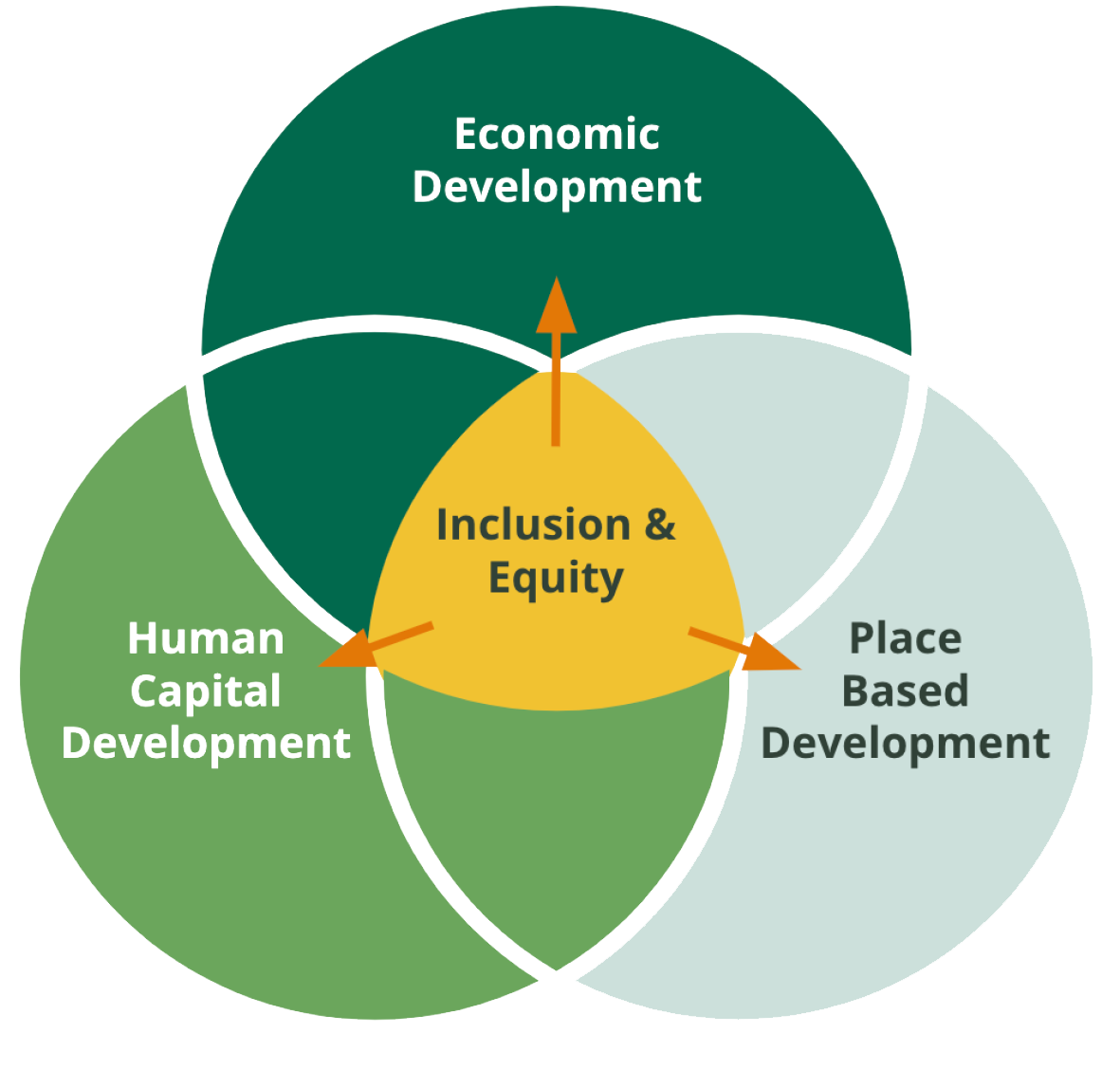
The Pillars Of Inclusive Regional Economic Development
Inclusive regional growth requires a strategic approach to addressing complex, cross-sector challenges, particularly in historically marginalized communities. This framework organizes efforts into three interconnected pillars: Economic Development, Human Capital Development, and Place-Based Development. Their overlap creates entry points for collaboration, ensuring inclusion remains central to building resilient, equitable economies that benefit all.
EQUITY AND INCLUSION
Equity and inclusion are a throughline, ensuring that community voices, needs, and participation shape each of these pillars is essential for achieving sustainable and just economic growth.
Examples include:
Community engagement
Equity-centered outcomes
Cross-sector partnerships
Centering community wellbeing
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
Economic development creates economic opportunities for individuals and communities by leveraging industrial strategies, strong connectivity, research, and innovation. These systems drive economic dynamism and asset-building, fostering long-term stability and growth.
Examples include:
Industrial strategies
Research and development
Business attraction and retention
Wealth and asset building
HUMAN CAPITAL DEVELOPMENT
Human capital development focuses on supporting and advancing people within local economies while strengthening social bonds that connect communities. It enhances workforce skills, well-being, and civic engagement to create a skilled labor force that drives economic progress.
Examples include:
Health and wellbeing
Education and training
Work experience
Education and innovation
Civic engagement and social networks
PLACE-BASED DEVELOPMENT
Place-based development improves infrastructure, housing, and public spaces to enhance accessibility and economic opportunity, ensuring regional well-being and connectivity.
Examples include:
Transit systems
Digital/broadband access
Housing and shared community spaces
Environmental justice Public infrastructure